Introduction to Economics 1 Ara 5. Deneme Sınavı
Toplam 19 Soru1.Soru
I. The marginal rate of substitution is the maximum amount of another good that a person is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of the good. II. Two goods are perfect complements when the marginal rate of substitution of one good for the other is constant. III. Two goods with right-angle indifference curves are perfect substitutes such as left and right shoes. Which of the given statements about marginal rate of substitution are true?
|
Only I |
|
Only II |
|
I and II |
|
I and III |
|
II and III |
I. The marginal rate of substitution is the maximum amount of another good that a person is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of the good. (True)
II. Two goods are perfect complements when the marginal rate of substitution of one good for the other is constant. (False, two goods are perfect substitutes when the marginal rate of substitution of one good for the other is constant.)
III. Two goods with right-angle indifference curves are perfect substitutes such as left and right shoes. (False, two goods with right-angle indifference curves are perfect complements such as left and right shoes.)
The answer is A.
2.Soru
What does 'the law of diminishing marginal utility' mean?
|
The additional utility derived from consuming successive units of a product will eventually increase as the rate of consumption increases. |
|
The additional utility derived from consuming successive units of a product will stays the same as the rate of consumption increases. |
|
The additional utility derived from consuming successive units of a product will be zero as the rate of consumption increases. |
|
The additional utility derived from consuming successive units of a product will eventually decline as the rate of consumption increases. |
|
The additional utility derived from consuming successive units of a product will be infinite as the rate of consumption increases. |
The law of diminishing marginal utility is that the marginal (or additional) utility derived from consuming successive units of a product will eventually decline as the rate of consumption increases. The answer is D.
3.Soru
Which of the following statements is true about the total revenue from sales in case of price changes of goods?
|
If demand is elastic, an increase in price causes total revenue to increase. |
|
If demand is elastic, a decrease in price, causes total revenue to decrease. |
|
When demand is inelastic, an increase in price cause total revenue to decrease. |
|
When demand is inelastic, an increase in price causes total revenue to stay the same. |
|
If demand is elastic, an increase in price causes total revenue to decrease. |
The answer of this question is related to the price elasticity of demand. If demand is elastic, an increase in price causes total revenue to decrease. A decrease in price, in contrast, causes total revenue to increase. On the other hand, when demand is inelastic, an increase in price causes total revenue to increase. With an inelastic demand curve, the reason that total revenue increases with price increase since the increase in price leads to a decrease in quantity demanded that is proportionally smaller. The correct answer is E.
4.Soru
Which of the following factor cannot be listed as one of the determinants of the Price Elasticity of Demand?
|
whether close substitutes are available, |
|
the good is necessity of luxury for the consumer, |
|
share (weight) of the good’s cost in the consumers’ budget, |
|
the time period. |
|
The importance of being important. |
Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand
The price elasticity of demand for a good or service depends on many factors such as whether close substitutes are available, the good is necessity of luxury for the consumer, share (weight) of the good’s cost in the consumers’ budget, and the time period.
5.Soru
Production technique A allows a firm to produce more goods than technique B without increasing the amount of inputs and energy used, what term is used to describe technique A in this situation?
|
Efficiency |
|
Equity |
|
Availability |
|
Frontier |
|
Edge |
If production technique A allows for production of more goods than technique B without increasing the amount of inputs and energy used, for example, technique A is said to be more efficient than technique B. For this reason the correct answer is “A”.
6.Soru
Which of the following is true?
|
Demand is elastic when the percentage change in quantity demanded is smaller than the percentage change in price. |
|
Inelastic demand always takes a value between zero and -1. |
|
Elastic demand always takes a value between zero and -1. |
|
Ineastic demand has an absolute value greater than 1. |
|
Demand is inelastic when the percentage change in quantity demanded is larger than the percentage change in price. |
Inelastic demand always takes a value between zero and -1.Elastic demand has an
absolute value greater than 1. Demand is inelastic when the percentage change in quantity demanded is smaller than the percentage change in price. Demand is elastic when the percentage change (decrease) in quantity demanded is larger than the percentage change
(increase) in price. Answer is B.
7.Soru
If a demand curve is vertical, which of the following statement is correct about its slope and its price elasticity?
|
If the demand curve is vertical, its slope and its price elasticity is infinite, |
|
If the demand curve is vertical, its slope is zero but its price elasticity is infinite, |
|
If the demand curve is vertical, its slope and its price elasticity is zero, |
|
If the demand curve is vertical, its slope and its price elasticity is equal to one, |
|
If the demand curve is vertical, its slope infinite but its price elasticity is zero. |
Shape of Demand Curves and Elasticity
The price elasticity of demand is closely related to the slope of the demand curve but the slope of a demand curve is different from its price elasticity of demand. However, there are exceptions in which the price elasticity of demand can be understood by looking at the slope of the demand curve. These cases are: (i) when price and quantity are identical, by looking at the slopes of the two intersecting demand curves it can be said which one is more elastic than the other. (ii) If the demand curve is vertical, its slope and its price elasticity is zero, and (iii) If the demand curve is horizontal, its slope and the price elasticity would be infinite.
8.Soru
Which of the following statement is correct about the slope and the shape of the demand curves?
|
Demand curves are downward sloping to reflect the negative relationship between the price and quantity demanded. Moreover, they are normally convex to the origin. |
|
Demand curves are upward sloping to reflect the positive relationship between the price and quantity demanded. Moreover, they are normally convex to the origin. |
|
Demand curves are upward sloping to reflect the positive relationship between the price and quantity demanded. Moreover, they are normally concave to the origin. |
|
Demand curves are downward sloping to reflect the positive relationship between the price and quantity demanded. Moreover, they are normally U-shaped. |
|
Demand curves are downward sloping to reflect the non-existence of the scarcity problem. Moreover, they are normally convex to the origin. |
Demand and Demand Curve
Demand curves are downward sloping to reflect the negative relationship between the price and quantity demanded. Moreover, they are normally convex to the origin. However, economists usually draw them as straight lines. It is ironic that these lines are still called curves, but we will follow the same convention and call them demand curves whether they are really curves or are lines.
9.Soru
Which blue point on the indifference curve above indicates the highest level of consumption?
|
I |
|
II |
|
III |
|
IV |
|
V |
Any point that is located above and to the right of an indifference curve provides a higher level of consumption of each good than the points on that indifference curve. Because of this, point V provides a higher level of utility than the points on the indifference curve. Thus, point V would be preferred to either point II, III or IV. The point that lies below and to the left of the indifference curve (point I), however, provides a lower level of utility. The correct answer is E.
10.Soru
In a two good economy with goods X and Y and income level I, which of the following represents the equation for a budget constraint?
|
Px.Y + Py.X = I |
|
Px.X + Py.Y = I |
|
w.L+r.K=C |
|
w.K+r.L=C |
|
Y=C+I+G+NX |
Let’s consider the budget constraint facing an
individual who has a fixed level of income (I) that
can be used to buy two goods (X and Y) at fixed
prices (PX and Py). The budget constraint facing
this individual can be expressed as:
Px.X + Py.Y = I
The answer is B.
11.Soru
In which of the following situations is the service provided by product markets used?
|
When you buy a land. |
|
When you buy a yacht. |
|
When you buy a new car. |
|
When you buy a new sofa. |
|
When you buy a hamburger. |
There are two types of markets: product markets and factor markets. In product markets, all sorts of goods and services from cars to movie tickets are bought and sold. They refer to the market for the final goods themselves; however, factor markets are concerned with markets for factors of production or input in a production process, such as land, labor and capital. When you are offered a consumer loan, you are in a capital market. When you try to get a job, you are in a labor market. If you want to buy a piece of land or house by the Aegean coast for your retirement, then you are a participant in the land market or real estate market. The correct answer is A.
12.Soru
I. Limited income necessitates choice. II. One good cannot be substituted for another. III. The law of diminishing marginal utility applies. Which of the statements are true for consumer behavior?
|
Only I |
|
Only II |
|
I and II |
|
I and III |
|
II and III |
The fundamental principles of consumer behavior are limited income necessitates choice, consumers make their decisions purposefully, one good can be substituted for another, consumers must make decisions without perfect information but knowledge and past experiences will help, the law of diminishing marginal utility applies. The true answer is D.
13.Soru
Which choice among the following is not a possible cause of market failures?
|
Positive externalities |
|
Market power |
|
External costs |
|
Inequity |
|
External benefits |
Inequity is not a couse of market failure
14.Soru
Which of the following happens when Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) happens?
|
Consumer starts investigating alternative products due to his or her limited budget. |
|
Consumer shifts from one product to another without questionning. |
|
Consumer's brand loyalty towards some brands increase consciously. |
|
When a consumer’s consumption increases, his or her openness to other products will increase as well. |
|
When a consumer’s consumption of good X increases, his or her valuation of good X relative to good Y will decline. |
Consumers differ in the importance that they attach to an extra unit of a particular good. This is useful in getting a measure of the relative importance attached by the consumer to the acquisition of another unit of a particular good. This means that whereas a consumer’s consumption of good X increases (and his or her consumption of good Y declines), his or her valuation of good X relative to good Y will decline. Besides, MRS is defined as the number of units of good Y that must be given up if the consumer, after receiving an extra unit of good X, is to maintain a constant level of satisfaction or utility.
15.Soru
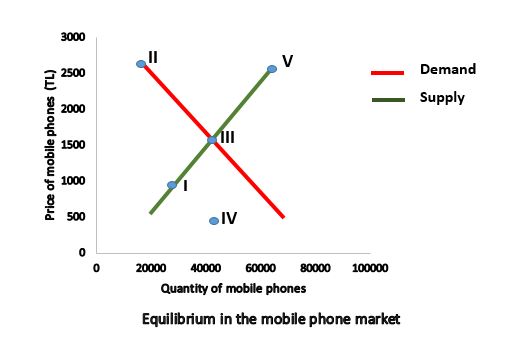 Which blue point shows the equilibrium in this mobile phone market?
Which blue point shows the equilibrium in this mobile phone market?
|
I |
|
II |
|
III |
|
IV |
|
V |
The concept of equilibrium is central in economics. Equilibrium can be defined as a situation in which the supply and demand equals to each other. In other words, it is the price level at which demand and supply curves intersect. At this price level, the quantity demanded will be equal to the quantity supplied. The correct answer is C.
16.Soru
Minimum wage is an example of:
|
Price ceiling. |
|
Price floor. |
|
Tax incidence. |
|
Consumer surplus. |
|
Market efficiency. |
As a social policy, the minimum wage laws are imposed to create a fair minimum wage floor to protect workers in the job market. While the intention of the policymakers is to protect the workers, the imposition of minimum wage laws creates unemployment for especially unskilled labors. Price floor is a legal minimum on the price at which a good or service can be sold.
17.Soru
Which of the following illustrates how much of a specific good an individual
or household would be willing to buy at different prices?
|
Demand curve |
|
Supply curve |
|
Aggregate demand |
|
Aggregate supply |
|
Production possibility frontier |
A demand curve is a graph that illustrates how much of a specific good an individual or household would be willing to buy at different prices. The answer is A.
18.Soru
Assume that you increase the total number of meatballs eaten from 10 to 11. What is the 'marginal' increase in this example?
|
1 |
|
10 |
|
11 |
|
0.10 |
|
0.11 |
Eating one more meatball at dinner (increasing the total number of meatballs eaten from 3 to 4).That last meatball is called marginal as they are additions at the edge. The answer is A.
19.Soru
Which of the goods or services below is expected to have a large income elasticity?
|
Bread |
|
Dental care |
|
Jewelry |
|
Clothing |
|
Water |
Necessities, such as food, clothing, health services and gasoline tend to have small income elasticities since consumers, regardless of their income levels, chose to buy these items. Luxuries on the other hand tend to have large income elasticities. The correct answer is C.
-
- 1.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 2.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 3.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 4.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 5.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 6.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 7.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 8.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 9.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 10.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 11.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 12.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 13.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 14.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 15.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 16.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 17.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 18.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 19.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ


