Introduction to Economics 1 Ara 9. Deneme Sınavı
Toplam 20 Soru1.Soru
What does 'a diminishing marginal rate of substitution' assumption imlpy?
|
A concave indifference curve |
|
A convex indifference curve |
|
A horizontal indifference curve |
|
A vertical indifference curve |
|
A linear indifference curve |
A diminishing marginal rate of substitution is exhibited when indifference curves are convex, and the slope of the indifference curve increases (becomes less negative) as we move down along the curve. The answer is B.
2.Soru
Which of the following refers to a graph which illustrates how much of a good firm is willing to sell at different prices?
|
Ceteris paribus |
|
Market supply curve |
|
Market demand curve |
|
Individual demand curve |
|
Individual firm’s supply curve |
Ceteris Paribus is a Latin phrase, which means “other things being equal.” It is used in economics to state that all variables other than the one studied are assumed to be constant or fixed. A demand curve is a graph that illustrates how much of a specific good an individual or household would be willing to buy at different prices. Market demand is the sum of all the quantities of a product demanded per period by all the buyers in the market. A supply curve is a graph which illustrates how much of a good a firm is willing to sell at different prices. In this question it is mentioned about supply curve, and the supply curve of an individual firm. The correct answer is Choice E.
3.Soru
For a price P1=100, quantity demanded of a good is Q1=20. Then the price increases, and it becomes P2=150. Quantity demanded decreases to Q2=8. The price elasticity of demand using the mid-point approach is approximately:
|
-7,8 |
|
0 |
|
10,3 |
|
-2,1 |
|
-1 |
Using the mid-point approach, the formula to calculate the price elasticity of demand is:(Q2 -Q1 )/(Q2 +Q1 )/ 2 divided by (P2 - P1 )/(P2 + P1 )/2. Using this formula, the result is -2,1.
4.Soru
Frank plans to take his family away on holiday. Considering the fact that he has a crowded family, and he is the only person working in his family, he decides to book a bed and breakfast hostel. Which fundamental principle of consumer behaviors is applied by Frank?
|
Consumers make their decisions purposefully |
|
One good can be substituted for another. |
|
Consumers must make decisions without perfect information. |
|
Limited income necessitates choice. |
|
The law of diminishing marginal utility applies. |
Limited income necessitates choice. The main assumption of scarcity in economic theory states that we all have limited incomes. Limited income forces us to make choices about which goods we will and will not purchase. This will keep us within our budget. When more of one good or service is purchased, we must purchase less of some other good.
5.Soru
Which of the following describes the market failure?
|
An action or an effort to produce or avoid an outcome |
|
Effects of a production or a consumption to bystanders |
|
Substantial influence of a single buyer or seller in a market |
|
Inability to allocate resources efficiently |
|
Inability to produce all the desired goods and services |
Market Failures and Externalities
While the market mechanism generally leads to an efficient allocation of resources, markets sometimes fail to achieve that. Economists call it a market failure when the market itself falls short of allocating resources efficiently.
6.Soru
- Inelastic demand always takes a value between zero and -1.
- Elastic demand has an absolute value greater than 1.
- Demand is inelastic when the percentage change in quantity demanded is smaller than the percentage change in price.
- Demand is elastic when the percentage change (decrease) in quantity demanded is larger than the percentage change (increase) in price.
Which of these statements about the shape of demand curves and elasticity are true?
|
I, II and III |
|
I, III and IV |
|
I, II and IV |
|
II, III and IV |
|
I, II, III and IV |
Demand is inelastic when the percentage change in quantity demanded is smaller than the percentage change in price. Inelastic demand always takes a value between zero and -1.
Demand is elastic when the percentage change (decrease) in quantity demanded is larger than the percentage change (increase) in price. Elastic demand has an absolute value greater than 1.
7.Soru
Under ceteris paribus conditions, which of the following factor does determine the slope and the curvature of the demand curve?
|
changes in tastes and preferences, |
|
changes in prices, |
|
changes in prices of related goods, |
|
changes in income |
|
population and expectations. |
Determinants of Demand
The nature, the slope and the position of the demand curve are determined by different factors. The slope and the curvature of the demand curve are the consequences of consumer responses to the changes in prices under ceteris paribus conditions. There are two channels in which these responses are shaped: Income effect and substitution effect.
8.Soru
For a normal good, which of the following is true?
|
Income elasticity is zero |
|
Income elasticity is less than zero |
|
Income elasticity is greater than zero |
|
Price elasticity is zero |
|
Price elasticity is greater than zero |
For normal goods,the income elasticity is greater than zero and price elasticity is negative
For inferior goods,the income elasticity is less than zero. Answer is C.
9.Soru
What is illustrated by Phillippes curve?
|
Marginal revenue and marginal cost |
|
Cause of inflation and its harmful effects |
|
Purchasing power and high inflation |
|
Money supply and high inflation |
|
Tradeoff between inflation and unemployment |
A Phillips curve shows the tradeoff between unemployment and inflation in an economy. While this relationship examined first by the British economist William Phillips raised much controversy in economics in the past, most economists today recognize the possibility of the presence of a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment at least in the short-run. The correct answer is E.
10.Soru
8. Suppose that the income of a person who wants to buy a car has increased. If this person prefers to buy a higher priced car instead of the car which he/she decided to buy before the increase in his/her income, what good is the car previously decided to buy called?
|
Inferior |
|
Normal |
|
Complementary |
|
Of choice |
|
Ordinary |
A product is said to be inferior if the demand for that product goes down when the income of the consumers increases. Consumers prefer to buy higher priced substitutes in place of the inferior goods when their income rises. Examples of inferior goods may be ordinary (white) bread, cheap cheese (“lor”) or fake brand (imitation) jeans. If income increases, the demand curve for the inferior good will shift down to the left. When income reaches a certain level, the consumer buys only the higher quality goods and the demand for the inferior good will become zero. Inferior goods are the goods for which the demand falls when the income goes up. As it is understood the correct answer is “A”. Normal goods are the goods for which the demand increases when income is higher and decreases when income is lower. Two goods are said to be complements if they are generally or necessarily consumed together, such as tea and sugar cubes or printers and ink cartridges. Of choice means preferred. Ordinary means normal or average, and not unusual or special.
11.Soru
For what type of goods the demand increases when income is higher and decreases when income is
lower.
|
Substitute Goods |
|
Inferior Goods |
|
Complementary Goods |
|
Public Goods |
|
Normal Goods |
Normal goods are the goods for which the demand increases when income is higher and decreases when income is lower.
12.Soru
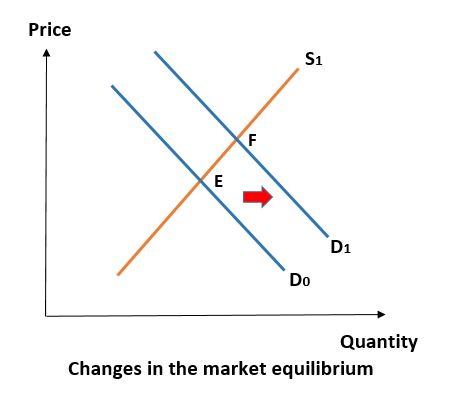 Which of the following statements is true regarding the market equilibrium graph above?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the market equilibrium graph above?
|
The price of the product increases because of changes in demand. |
|
The supply of the product increases despite the fall in the demand. |
|
The demand for the product decreases because of high prices. |
|
The price of the product decreases despite the fall in the supply. |
|
The supply of the product decreases because of a fall in prices. |
In our sample graph, the demand curve shifts to the right (from D0 to D1), so it illustrates the change in market equilibrium when the demand shifts. The graph shows that the market is initially in equilibrium at point E. When the demand increases, the demand curve shifts to the right and a new equilibrium is established in the intersection of the new demand curve and supply curve at point F. This point is characterized by a new price and a new quantity representing both demand and supply. This new price is of course higher than the initial price. The correct answer is A.
13.Soru
What is the difference between the price at which a firm sells its product and the cost of production?
|
Consumer surplus |
|
Producer surplus |
|
Total Surplus |
|
Market Efficiency |
|
Tax Incidence |
Producer surplus is the difference between the price at which a firm sells its product and the cost of production.
14.Soru
What is the property of a resource allocation of maximizing the total surplus received by the society?
|
Elasticity |
|
Efficiency |
|
Tax Incidence |
|
Price floor |
|
Price ceiling |
Efficiency is the property of a resource allocation of maximizing the total surplus received by the society
15.Soru
6. A manufacturing company determined the sum of all the quantities of a product demanded per period by all the buyers in the market. What demand can be said to have been determined?
|
Utility |
|
Individual |
|
Market |
|
Inferior |
|
Substitute |
The individual demand is derived from the solution of a personal utility maximization problem. Utility that the individual obtains from each additional or marginal unit consumed of a good declines, as more and more of that good is consumed. The consumer is said to be satiated after consuming a large enough quantity. Market demand is the sum of all the quantities of a product demanded per period by all the buyers in the market. A product is said to be inferior if the demand for that product goes down when the income of the consumers increases. If two products are substitutes for each other, a change in the price of one product will change the demand for the other product in the opposite direction. As it is understood from the information the correct answer is “C”.
16.Soru
People tend to buy inferior goods less when their income increases because ......... . Which of the following completes the sentence above correctly?
|
they are not easily found in the market |
|
they are not needed anymore |
|
they are already low in quality |
|
they are uninteresting to consumers |
|
they are not the sign of prosperity |
If a consumer buys less of a good when his or her income rises, the good is called an inferior good. In other words, inferior goods will have better quality alternatives. Therefore, when income rises, people can afford to forego the cheap alternative and buy the higher quality good instead. The correct answer is C.
17.Soru
Which of the following types of market systems faces a perfectly elastic demand curve?
|
Perfect competition. |
|
Monopolistic competition. |
|
Oligopoly. |
|
Monopoly. |
|
Monopsony. |
A perfectly elastic demand curve which would have a horizontal shape indicates “extreme price sensitivity” which means that the tiniest price increase causes the demand to fall to zero for the analyzed good. In economic theory, a good example of a perfectly elastic demand curve is the demand curve that firms face in competitive markets. The reason why competitive firms face a perfectly elastic demand curve is that elasticity is greater when there are lots of close substitutes available. In this case, the competitive firm is selling a product that has many perfect substitutes since in the competitive markets, by definition, there are many sellers and all sellers sell identical products
18.Soru
Which of the following is a positive statement?
|
When the government sets unemployment insurance payments too generously, for instance, it reduces the rewards for hard work, and may demotivate job seekers as a result. |
|
Government policies designed to improve equity may reduce efficiency. |
|
When large quantities of the national currency are put in circulation, the value (or purchasing power) of the money falls. |
|
The government that faces a tradeoff should set its priorities by giving the proper weights to these two goals that sometimes conflict. |
|
A household may have to decide whether to change the car or furniture at home. |
Positive statements in economics are statements that intend to describe how things are and how things actually work. A normative statement is a prescriptive statement, like the ones expected to be made by a policy adviser, involving normative judgements and prescriptions about how the world should be. As it can be understood from these definitions the correct answer is “C”.
19.Soru
Which of the following expression can represent the budget constraint facing an individual who has a fixed level of income (I) that can be used to buy two goods (X and Y) at fixed prices (PX and Py)?
|
Px + Py = I |
|
X + Y = I |
|
Px.X + Y = I |
|
Px.X + Py.Y = I |
|
Px/X + Py/Y = I |
BUDGET CONSTRAINT
Consumption choices are limited by income and prices. We summarize these influences on buying plans in a budget line or constraint. Given his or her tastes or preferences, along with the assumption of rationality of consumers, he or she tries to get on the highest possible indifference curve. To do so, the consumer must consider factors other than his or her own tastes or preferences or choices. These factors, such as prices of commodities and the level of the consumer’s income, can limit or constrain the nature and size of the market basket that he or she can buy.
Let’s consider the budget constraint facing an individual who has a fixed level of income (I) that can be used to buy two goods (X and Y) at fixed prices (PX and Py). The budget constraint facing this individual can be expressed as:
Px.X + Py.Y = I
20.Soru
Which of the following is true for microeconomics?
|
It studies how a country’s economy as a whole is structured and works |
|
It studies the aggregate effects of various policies pursued by the government |
|
It studies the effects of monetary policies pursued by the government |
|
It studies the behavior and decisions of individuals or households and firms |
|
It studies the effects of fiscal policies pursued by the government |
Microeconomics is the a main branch of economics that studies the behavior and decisions of the smallest decision units such as individuals or households and firms, whereas Macroeconomists study how a country’s economy as a whole is structured and works, by paying particular attention to the effects of monetary and fiscal policies pursued by the government. The answer is D.
-
- 1.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 2.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 3.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 4.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 5.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 6.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 7.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 8.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 9.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 10.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 11.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 12.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 13.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 14.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 15.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 16.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 17.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 18.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 19.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 20.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ


