Statıstıcs I Final 9. Deneme Sınavı
Toplam 20 Soru1.Soru
Which of the following is not a nominal variable?
|
Exam grade |
|
Gender |
|
Region of residence |
|
Field of study |
|
Type of transport |
The easiest form of data is called categorical, or qualitative. Categorical variables and data can be either nominal or ordinal. Exam grade is an ordinal categorical variable, since its categories are ordered: A is better than a B, B is better than a C, and so on. Other examples of nominal categorical variables are gender, region of residence, field of study, type of transport, type of housing, etc.
2.Soru
Which of the following is true about range?
|
The range of a data set is shown as R. |
|
Range is the difference between the largest and smallest values. |
|
It depends only on the highest and lowest observations. |
|
Range is heavily affected by these extremes values. |
|
Range informs about the variability of the observations. |
The disadvantage of the range is that it depends only on the highest and lowest observations and it tells us nothing about the variability of the observations which fall between the two extremes.
3.Soru
Which of the followings is generally demonstrated as P(m), where m is the number taking values between 0 and 100?
Which of the followings is generally demonstrated as P(m), where m is the number taking values between 0 and 100?
|
Range |
|
Percentiles |
|
Interquartile Range |
|
Variance |
|
Skewness |
The percentiles generally are demonstrated as P(m), where m is the number taking values between 0 and 100. Intuitively, the P(m) percentile of a set of n measurements, arranged in order of magnitude, is the value such m percent of the measurements are less than or equal to that corresponding value.
4.Soru
According to the following cumulative distribytion function graph, what is the probability of x < -1?
|
0.5 |
|
0.4 |
|
0.3 |
|
0.1 |
|
0 |
It will be zero.
5.Soru
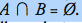 What does this equation tell us?
What does this equation tell us?
What does this equation tell us?
|
A and B are closely related two events |
|
The events A and B intersects |
|
A and B are mutually exclusive |
|
A and B are complementary events |
|
A and B are union of events |
If A and B are any two events then they are said to be mutually exclusive. The above equation shows this.
6.Soru
Which of the following is a measure of the dispersion or variability for data set for continuous random variables?
|
Mean |
|
Mode |
|
Median |
|
Variance |
|
Frequency |
The variance is a measure of the dispersion or variability for data set for continuous
random variables.
7.Soru
Data format : (class, class interval, frequency, cumulative frequency) ; data : (1, 100 up to 200, 5, 5), (2, 200 up to 300, 10, 14), (3, 300 up to 400, 16, 30), (4, 400 up to 500, 20, 50), (5, 500 up to 600, 10, 60) ; what is the 40th percentile of these data ?
|
355 |
|
357.5 |
|
360 |
|
362.5 |
|
365 |
k = 60 x 40 / 100 = 24 ; k is in the 3rd class ; P(k) = 300 + (100 / 16) (24 – 14) = 300 + 62.5 = 362.5 . pg. 117. Correct answer is D.
8.Soru
Which of the following is TRUE about symmetric bell-shape distributions?
|
Only the mean and median are the same value. |
|
The mean, median, and mode are all equal. |
|
The median falls between the mean and mode. |
|
The mean is smaller than median. |
|
The mode is larger than the mean. |
In symmetric distributions like bell-shape and rectangular (or uniform)
ones, the mean and median are the same value. The correct answer is B.97
9.Soru
Consider that continuous random variable X is uniformly distributed and takes values between 10 and 50. Find the probability of P (15 < X < 25) ?
|
0.10 |
|
0.15 |
|
0.20 |
|
0.25 |
|
0.30 |
f(x) = 1 / (b - a) = 1 / (50 - 10) = 1 / 40 ; P (15 < X < 25) = Int(15, 25)(f(x) dx) = Int(15, 25)((1/40) dx) = girdi(15, 25)((1/40) * x) = (1/40) * (25 - 15) = 1/4 = 0.25. pg. 186. Correct answer is D.
10.Soru
I. The mean is pulled in the direction of the tail.
II. The median falls between the mode and the mean.
III. The mean, median, and mode are all the same.
If the distribution is left skewed, having a long tail in negative direction and a single peak, which of the statements above are true?
|
Only I |
|
I and II |
|
I and III |
|
II and III |
|
I, II and III |
The measures of skewness are another kind of descriptive statistics and give information about the shape of distribution of the observations. A data set which is not symmetrically distributed is called skewed. The mainly observed shapes of distribution are symmetric, left skewed (negatively skewed), and right skewed (positively skewed). If the distribution is unimodal symmetric, the mean, median, and mode are all the same. If the distribution is left skewed, having a long tail in negative direction and a single peak, the mean is pulled in the direction of the tail, and the median falls between the mode and the mean. The correct answer is B.
11.Soru
Which of the followings cannot be given as an example for random experiments?
|
Rolling a fair die. |
|
Customers arriving at a particular store during some time interval. |
|
Airplanes taking off in a given time interval at some airport. |
|
Some particular customer requests in a bank. |
|
Surveying an elemanatry level english classroom. |
A random experiment is any process that leads to two or more possible outcomes, without knowing exactly which outcome will occur.
For example, when a fair die is rolled we know that one of the six faces will show up but we will not be able to say exactly which face will actually show up. Thus, rolling a fair die is an example of a random experiment. Some further examples of random experiments are:
• Customers arriving at a particular store during some time interval.
• Airplanes taking off in a given time interval at some airport.
• Some particular customer requests in a bank.
Note that in a random experiment, although we do not know which outcome will occur, we are able to list or describe all of the possible outcomes.The set of all possible outcomes is important to understand the random experiment. Terefore, it is called a sample space, which is restated below as a definition.
12.Soru
What is the geometric mean of the numbers 4, 25, 100 ?
|
100 |
|
102 |
|
104 |
|
106 |
|
108 |
The geometric mean is found by taking the square root of all the observation's multiplication. For 4, 25, 100 their multiplication is 4*25*100=10000 and the square root of 10000 is 100. The answer is A.
13.Soru
Which of the following can be categorized as a discrete random variable?
|
Water consumption in a company |
|
The speed of a car in a certain area |
|
Weighs of a people in a population |
|
electricity consumption of a house |
|
The number of students in a class |
While all variables can take real numbers in other options, the number of the students cannot take a real number in option E. That is the number of students in a class can only take uncountable numbers.
14.Soru
What is the area below the probability density function f (x) = 0.1, for 0 ? x ? 20 ?
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
The probability density function f (x) = 0.1 is a straight line above the values 0 to 20, therefore, it is a rectangle with one side being 0.1 value and the other 20. The area is calculated by 20*(0.1) which is equal to 2. The answer is A.
15.Soru
"For binomial distribution, its principal assumptions are n independent trials with two possible outcomes (success or failure) for each trial, and the success probability remains constant for each trial. On the other hand __________ distribution doesn’t involve with independence assumption for each trial and accordingly the sampling process is established on without replacement. Because of these features, it is broadly used in various real life applications especially for acceptance sampling in quality control."
Choose the correct option to complete blank in the paragraph given above.
|
Binomial |
|
Poisson |
|
Hypergeometric |
|
Standard |
|
Variance |
In binomial distribution, its principal assumptions are n independent trials with two possible outcomes (success or failure) for each trial, and the success probability remains constant for each trial. Therefore in binomial distribution the sampling process is carried out with replacement. On the other hand hypergeometric distribution doesn’t involve with independence assumption for each trial and accordingly the sampling process is established on without replacement. Because of these features, hypergeometric distribution is broadly used in various real life applications especially for acceptance sampling in quality control.The correct answer is C.
16.Soru
For an observation that results in values 6,7,2,4,3,5,6 what is the %30 trimmed (truncated) mean of the group?
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
10 |
The trimmed or as it may sometimes be called as the truncated mean is a slightly modified version of the
arithmetic mean. Trimmed or truncated mean is calculated after a certain number or proportion of the lowest and highest observations from the sorted data are removed (trimmed) from the calculations. First, the data is ordered from smallest to largest, as follows, 2,3,4,5,6,6,7. Then we will find how many data points will be discarded, k, since the trimming is 30% and there are 7 observations, the value of k is k = np = 7×0.30 = 2,1 which is nearly 2. Therefore two 2,3,6 and 7 is removed from the set, which yields to 4,5,6. The sum, 15 is divided to n - 2k which is equal to 7 - 2*2=3 this results in the value 5.The answer is D.
17.Soru
What is mode?
|
The most frequent score in a data set |
|
The gap between the lowest and the highest score |
|
The difference between a certain score and the average |
|
The score optained by dividing the total scores by the number of scores |
|
Scores which are turned into zvalue |
Mode is the most frequently appearing score in a data set.So the correct answer is A.
18.Soru
Data : 20, 12, 16, 12, 10 ; what is the Pearson’s coefficient of skewness of these data ?
|
0.80 |
|
-1.75 |
|
0.90 |
|
1.50 |
|
-1.20 |
median : 12 ; arithmetic mean : m = 70 / 5 = 14 ; s = ((42 + 22 + 22 + 22 + 62) / 4)1/2 = 4 ; Pearson’s coefficient of skewness PCS = 3 (14 – 12) / 4 = 1.5 . pg. 122. Correct answer is D.
19.Soru
A box contains 10 glasses : 4 red and 6 blue. Two glasses are selected randomly, without replacement, from this lot. What is the probability that the first selected glass is blue?
|
3 / 5 |
|
7 / 15 |
|
7 / 12 |
|
17 / 24 |
|
3 / 4 |
S = {BR , BB , RB , RR} ; C(10, 2) = 10! / (2! * (10-2)!) = 10! / (2! * 8!) = 10 * 9 / 2 = 45 ; P(BR) + P(BB) = (6 / 10) * (4 / 9) + (6 / 10).* (5 / 9) = 6 * 4 / (10 * 9) + 6 * 5 / (10 * 9) = 4 / 15 + 1 / 3 = 9 / 15 = 3 / 5. pg. 137. Correct answer is A.
20.Soru
According to empirical probability, which of the following statements is not true?
|
It uses the relative frequencies to assign the probabilities to the events. |
|
It is based on experiments. |
|
To find the probability of a specific event, the experiments are repeated many times. |
|
It states that all the outcomes have the same chance of happening. |
|
In empirical probability, the past information becomes very important. |
The empirical probability uses the relative frequencies to assign the probabilities to the events. The empirical probability is based on experiments. In order to find the probability of a specific event, the experiments are repeated many times and the observed outcomes of the event we are interested in is counted. We can formularize this by following equation
The more experiment we do, we may get better results for the probability that we are looking for.
The correct answer is D.
-
- 1.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 2.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 3.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 4.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 5.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 6.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 7.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 8.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 9.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 10.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 11.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 12.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 13.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 14.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 15.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 16.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 17.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 18.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 19.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 20.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ


