Statıstıcs I Final 8. Deneme Sınavı
Toplam 20 Soru1.Soru
What is the formula P(A?B) = P(A?B)P(B) called?
|
Classical Probability |
|
Empirical Probability |
|
Subjective Probability |
|
Multiplication rule |
|
Bayes’ Theorem |
Suppose that we know that event B has occurred and we are interested in finding the probability of event A. That is, we are interested in finding the probability of A knowing that event B has occurred. The formula specified is actually called the multiplication rule and has important applications.
2.Soru
2 models will be randomly selected to walk in a fashion show in France. There are 2 models from an Italian agency and 3 of them work for a Turkish agency. If the event “one Turkish model X and one Italian model Y is chosen” is denoted by E, which one below is the listing the elements of E?
|
E= {X1X2, Y1Y2, Y1Y3, Y2Y3, X1Y1, X1Y2, X1Y3, X2Y1, X2Y2, X2Y3} |
|
E = { X1Y1, X1Y2, X1Y3, X2Y1, X2Y2, X2Y3} |
|
E = { X1Y1, X1Y2, X1Y3, X2Y1, X2Y2} |
|
E = { X1X1, X1Y2, X1Y3, X2Y1, X2Y2, X2Y3} |
|
E = { X1Y1, X1Y2, X1Y3} |
E = { X1Y1, X1Y2, X1Y3, X2Y1, X2Y2, X2Y3}
3.Soru
At a local district, there are three different pizza restaurants denoted here by A, B, and C. It is known that 40% of all customers give an order from company A, whereas 35% give an order from company B, and 25% give an order from company C. It is also known that 10% of the motorcycles from company A, 20% of the motorcycles from company B, and 5% of the motorcycles from company C need to a checkup before the next pizza delivery. If a motorcycle returned to the company needs a checkup before the next pizza delivery, what is the probability that this motorcycle was owned by company B?
|
0,58 |
|
0,62 |
|
0,74 |
|
0,81 |
|
0,93 |
P(A)=0.40 P(U/A)=0.10 P(U/A).P(A)=0.04
P(B)=0.35 P(U/B)=0.20 P(U/B).P(B)=0.07
P(C)=0.25 P(U/C)=0.05 P(U/C).P(C)=0.0125
P(U)= 0,04+0,07+0,0125=0,12
P(B/U)=0,07/0,12=0,58
4.Soru
Probability density function for continuous random variable X is defined as follows;
f (x) = 0.05, for 0 ? x ? 30.
Which of the following is the standard deviation of this function?
Probability density function for continuous random variable X is defined as follows;
f (x) = 0.05, for 0 ? x ? 30.
Which of the following is the standard deviation of this function?
|
14,08 |
|
14,06 |
|
14,05 |
|
15,07 |
|
14,03 |
µ=E(X)= ?xf(x)dx
?2 =V(x)=E(X-µ)2 = ?(x-µ)2 f(x)dx= ?x2 f(x)dx-µ2
The standard deviation of random variable X is a square root of variance= 14.03
5.Soru
A bakery employs 10 people. The number of years’ experience that the employees of the company have is the following: 0, 0, 2, 4, 5, 8, 15, 17, 20, 24. What is the 80th percentile of the data?
|
18,5 |
|
19,5 |
|
20,5 |
|
21,5 |
|
22,5 |
6.Soru
Pdf for continuous random variable X is defined as follows;
f (x) = 0.02, for 0 ? x ? 50. What is the standard deviation of the continuous random variable X?
|
208.33 |
|
833.33 |
|
104.167 |
|
14.4336 |
|
0. 1443 |
The standard deviation of the continuous random variable X;
7.Soru
I. It carries a unique numerical value.
II. It is determined by random probability experiment and its associated outcome
III. In statistical notation, random variables represented by lower case such as x and y.
Which of the following statements above are TRUE for random variables?
|
I, II and III |
|
I and II |
|
I and III |
|
Only I |
|
Only II |
In statistical notation random variables represented by capital letters such as X,Y and so on. So number III is false. Number I and II are true. The correct answer is B.
8.Soru
Consider that continuous random variable X is uniformly distributed and takes values between -5 and b and the mean value of µ = 10. Determine the value of b?
|
0 |
|
5 |
|
10 |
|
20 |
|
25 |
f(x) = 1 / (b - a) ; E(X) = (a + b) / 2 = (-5 + b) / 2 = 10 ; b = 25. pg. 186. Correct answer is E.
9.Soru
What can be said true about the basic concepts of probability?
|
An event occurs if the random experiment results in one of the basic outcomes of that event. |
|
A set of some of the possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the sample space. |
|
Each possible outcome of a random experiment is called a sample space. |
|
The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the elementary outcome. |
|
A random experiment is any process that leads to a certain possible outcome. |
A random experiment is any process that leads to two or more possible outcomes, without knowing
exactly which outcome will occur. The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the sample space. Each possible outcome of a random experiment is called an elementary outcome. An event occurs if the random experiment results in one of the basic outcomes of that event. A is the correct answer.
10.Soru
I. P(A+B) = P(A?B)P(B) this formula is called the multiplication rule.
II. A and B are statistically independent if and only if P(A+B) = P(A)P(B).
III. For A and B sets independence can also be denoted by P(A?B)
|
Only I |
|
Only II |
|
I and II |
|
I and III |
|
II and III |
I. P(A+B) = P(A?B)P(B) this formula is called the multiplication rule. (True)
II. A and B are statistically independent if and only if P(A+B) = P(A)P(B). (True)
III. For A and B sets independence can also be denoted by P(A?B). (False, P(A?B) denotes conditional probability for sets A and B.)
The answer is C.
11.Soru
A random experiment is any process that leads to two or more possible outcomes, without knowing exactly which outcome will occur. Which one below is NOT an example of a random experiment?
A random experiment is any process that leads to two or more possible outcomes, without knowing exactly which outcome will occur. Which one below is NOT an example of a random experiment?
|
Rolling a fair die |
|
Customers arriving at a particular store during some time interval. |
|
Airplanes taking off in a given time interval at some airport. |
|
The students in the biggest classroom at school. |
|
Some particular customer requests in a bank. |
A random experiment is any process that leads to two or more possible outcomes, without knowing exactly which outcome will occur.
For example, when a fair die is rolled we know that one of the six faces will show up but we will not be able to say exactly which face will actually show up. Thus, rolling a fair die is an example of a random experiment. Some further examples of random experiments are:
-
Customers arriving at a particular store during some time interval.
-
Airplanes taking off in a given time interval at some airport.
-
Some particular customer requests in a bank.
12.Soru
I. 0 ? F (x) ? 1
II. If x1 ? x2 then F (x1) ? F (x2)
III. If x1 = x2 then F (x1) = F (x2)
Which of the given statements are considered the properties of the cumulative probability function?
|
Only I |
|
Only II |
|
I and II |
|
I and III |
|
II and III |
I. 0 ? F (x) ? 1 (True)
II. If x1 ? x2 then F (x1) ? F (x2) (True)
III. If x1 = x2 then F (x1) = F (x2) (False, If x1 ? x2 then F (x1) ? F (x2))
The answer is C.
13.Soru
z score of a standard normally distributed random variable Z for value=-a is 0.195. What is P(Z < (-a)) ?
|
0.805 |
|
0.695 |
|
0.305 |
|
0.265 |
|
0.195 |
-
P(Z < (-a)) = P(Z > a) = 0.5 – 0.195 = 0.305 . pg. 193. Correct answer is C.
14.Soru
A six-sided fair dice has been thrown 1000 times and the occurrence of number 2 is 156. What is the empirical probability of obtaining a number 2 when you throw a six-sided fair dice?
|
0,156 |
|
0,159 |
|
0,240 |
|
0,300 |
|
0,500 |
Empirical Probability of an Event = The number of times the event happens/Total number of observations
P (Number 2)= 156 / 1000 =0,156
15.Soru
A manager in a company has two assistant directors. The probability that the older assistant director comes late to work on a given day is 0.07, whereas for the younger assistant director this probability is 0.05. In addition, the probability that both assistant directors come late to work on given day is 0.03. What is the probability that on a given day one or both assistant directors come late to work?
|
0.87 |
|
0.97 |
|
1.07 |
|
1.17 |
|
1.27 |
Note that this event corresponds to (O+Y –) , ( – O+Y – ) , ( – O+Y – ), and that (O+Y –) , ( – O+Y – ) , ( – O+Y – ) , (O+Y ) = S.
Therefore, P((O+Y – ) , ( – O+Y –) , ( –O+Y–)) = 1 – P(O+Y– ) = 1 – 0.03 = 0.97 The correct answer is B.
16.Soru
Which one below is NOT one of the differences between continuous and discrete random variables?
|
Continuous random variables take on uncountable and infinite number of possible outcomes. |
|
Probabilities in continuous random variables can be determined from the area under probability density function. |
|
The range of continuous random variable X comprises all real numbers in an interval. |
|
To describe such structures through continuous random variables density functions are utilized. |
|
Only in continuous random variables, the mean is a measure of the midpoint or center of the probability distribution. |
A major difference between continuous and discrete random variables is the former takes on uncountable and infinite number of possible outcomes in a given interval. Hence the range of continuous random variable X comprises all real numbers in an interval.
In contrast to discrete random variables, probabilities in continuous random variables can be determined from the area under probability density function (pdf) which is represented by f (x).
Similar to the discrete random variable the mean is a measure of the midpoint or center of the probability distribution and the variance is a measure of the dispersion or variability for data set for continuous random variables.
17.Soru
- Commerce, especially online electronic commerce
- Finance, for example share prices on stock markets, all managed electronically
- Insurance, all the premiums, incidents, actuarial transactions in an insurance company
- Transport, for example in the airline industry, all the flights, all the passengers
Which of the above can be considered for big data?
|
I, II and III |
|
I, III and IV |
|
I, II and IV |
|
II, III and IV |
|
I, II, III and IV |
What are the “big data” sets today and where do they come from? These are mostly found in the following areas:
- Commerce, especially online electronic commerce
- Finance, for example share prices on stock markets, all managed electronically
- Insurance, all the premiums, incidents, actuarial transactions in an insurance company
- Biomedicine, especially in genetics, where information is literally exploding as gene-sequencing reveals and codes the total genetic profile of a person
- Transport, for example in the airline industry, all the flights, all the passengers
- Climate data, measurements from tens of thousands of weather stations across the world
18.Soru
z score of a standard normally distributed random variable Z for value=a is 0.1700. What is P(Z > a) ?
|
0.17 |
|
0.25 |
|
0.33 |
|
0.67 |
|
0.83 |
P(Z > a) = 0.5 – 0.17 = 0.33. pg. 193. Correct answer is C.
19.Soru
Let E1, E2, ..., Ek be a collection of mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive events. Then for any event A with P(A)=?0 and any i=1, 2..., k
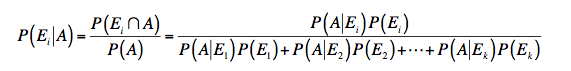
What is the formula above?
Let E1, E2, ..., Ek be a collection of mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive events. Then for any event A with P(A)=?0 and any i=1, 2..., k
What is the formula above?
|
Multiplication rule |
|
Bayes’ Theorem |
|
Random experiment |
|
Elementary outcome |
|
Independence probability |
An important application of conditional probability is given in the following result, which is known as Bayes’ Theorem.
Let E1, E2, ..., Ek be a collection of mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive events. Then for any event A with P(A)=?0 and any i=1, 2..., k
P(Ei A)=P(Ei?A)= P(AEi)P(Ei)
P (A) P (A E1 )P (E1 )+ P (A E2 )P (E2 )+!+ P (A Ek )P (Ek )
20.Soru
In ___________ approach, the researcher assigns a suitable value as the probability of the event.
Which of the following fills the blank correctly?
|
Mutual Probability |
|
Classic Probability |
|
Empirical Probability |
|
Objective Probability |
|
Subjective Probability |
Sometimes it may not possible to observe the outcomes of events; therefore, the researcher may assign a probability to an event. In subjective probability approach, the researcher assigns a suitable value as the probability of the event. Therefore, a personal judgment comes in to play to assign the probability. This approach is not favorable method to assign probability, but sometimes if there’s no previous knowledge on the subject then the researcher may assign a subjective probability as a starting point.
-
- 1.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 2.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 3.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 4.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 5.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 6.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 7.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 8.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 9.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 10.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 11.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 12.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 13.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 14.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 15.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 16.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 17.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 18.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 19.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ
- 20.SORU ÇÖZÜLMEDİ


